| RESEARCH IT! >> IPO BUZZ! | |
Andhra Bank
|
| Issue Summary |
|
|
| Background |
| Business | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The bank has a total of 1,018 branches spread across the country. Present day banking being technology driven, the bank has 201 totally computerized branches and 158 partially computerized branches as on 8th December 2000. The bank also has recorded significant growth in the year FY00. Its net NPAs was 3.5% of the net advances as on 31st March 2000. The total deposits of the bank stood at Rs 145 bn as against the Rs 104 bn during the previous year. The gross bank credit of the bank also increased from Rs 48 bn to Rs 59 bn, registering a growth rate of 22% in FY00. As on 30th September 2000, gross credit stood at Rs 62 bn, thus registering a growth rate of 26% on an annualised basis.
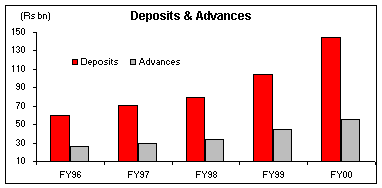 The share of the priority sector advances, as percentage to net bank credit was 45% as against a stipulated norm of 40%. The outstanding credit of the bank under priority sectors increased by 24%, i.e. Rs 23 bn in FY00.
The bank has planned for a subsidiary of a primary dealer in Government securities with an Initial Capital of Rs 1 bn. The bank has applied to Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for setting up the subsidiary. The Bank targets a growth rate of 40% during 2000-2001 with a thrust on corporate finance, retail lending, education, housing, and personal banking loans. The bank is planning for networking 100 branches in top business centres in the country. The main objectives of this public issue are:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Promoters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dr. Bhogaraju Pattabhi Sitaramaiah founded the bank in 1923. The bank started its operations at Machilipatnam, a port town in Coastal Andhra and was nationalised in FY80. | Sector | |
| The banking sector has seen far-reaching changes in recent years. The RBI has, in keeping with the recommendations of the Narasimham Committee, raised the minimum Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) from the level of 8% to 9% with effect from March 31, 2000. The rise in CAR was accompanied by tightening of norms of non-performing assets, making profitability and competence of banks a hallmark at a time when banks are facing tight spread. Since the government freed the interest rates on deposits for over 15 years coupled with the withdrawal of restrictions regarding uniform rates for the same maturity period deposits, competition has really intensified in the Indian banking sector. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reasons to apply |
The net NPAs of the Bank are relatively low at 3.5% of the net advances as on 31st March 2000. This is also lower than the average NPA level of 7.9% for all the public sector banks. The bank is taking steps to reduce the NPA level through aggressive recovery drive, initiating proactive steps to arrest the slippage of NPAs combined with improved risk management practices. The net NPAs of the bank as on 30th September 2000 have decreased to 3.2%.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Apart from conventional lending and borrowing, the bank has other diversified business, which include credit cards, housing finance (through Andhra Bank Housing Finance Limited) and merchant banking.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The bank has branch network of 1018 branches well spread across the country of which, 384 are rural branches, 285 are semi-urban branches, 225 urban branches and 124 metropolitan branches. It also has specialised branches totaling 21 to cater other services like agriculture, small-scale industries, industrial finance and high tech branches.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The bank's capital adequacy ratio was 12.5% as on September 30, 2000, as against the minimum requirement of 9% as specified by RBI.
|
| Reasons not to apply |
The Indian banking sector is undergoing large-scale consolidation, wherein bigger banks are merging or acquiring smaller banks to command better economies of scale and to increase their retail presence. Moreover, private sector banks are generally more aggressive and have more control over decision-making process than public sector undertaking. This is apparent from the fact that the market share of private banks have gone up considerably than state owned banks. Therefore, the intensity of competition is very high because private banks have upper hand in terms of value added services.
| |
As on 30th September 2000, there were 324 cases involving writ petitions filed by employees, suits and consumer cases with an aggregate claim of Rs 3.4 bn. Out of these, the contingent liabilities were above Rs 10 million in 10 cases. Moreover, various proceedings against the bank involving income tax liabilities of Rs 387 m are also pending in appeal with IT authorities.
| |
Going forward, keeping in mind the competition in perspective, interest spread i.e. difference between cost of deposits and yield on advances, would become thinner and thinner.
|
| Financial Performance |
| (Rs bn) | FY98 | FY99 | FY00 |
| Interest earned | 9.2 | 10.5 | 14.4 |
| Other Income | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.3 |
| Total Income | 10.3 | 12.0 | 16.7 |
| Interest expenditure | 6.1 | 7.2 | 10.3 |
| Other expenditure | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.6 |
| EBDIT | 3.1 | 3.4 | 4.2 |
| OPM (%) | 33.9% | 31.9% | 28.8% |
| Provisions | 0.8 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Net profit | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.2 |
| NPM (%) | 8.2% | 8.7% | 8.4% |
| Issued shares (bn) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| EPS (Rs) | 2.2 | 2.6 | 3.5 |
| P/E (x) | 4.6 | 3.8 | 2.9 |
| Key Ratios | |||
| % of Net NPA / Net advances | 2.9% | 4.3% | 3.5% |
| Credit / Deposit ratio | NA | 43.0% | 39.0% |
| Yield on Advances (%) | 12.7 | 12.6 | 12.3 |
| Cost of deposits (%) | 8.1 | 8.3 | 8.7 |
| Interest Spread (%) | 4.6 | 4.4 | 3.6 |
| Funding |
| Shareholding |
| Particulars | Pre-Offer | Post-Offer |
| Govt. of India | 100.00 | 66.7 |
| Public | - | 33.3 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 |